HOLSYS - EEBLab
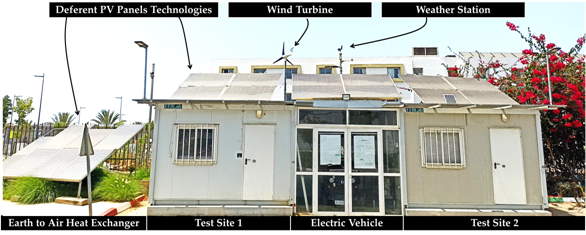
The EEBLAB has been made essentially for implementing and testing different scenarios related to Energy efficiency, ICT, and renewable energies integration and control. The aim is to first validate the deployed prototypes for final deployment and long-run assessment at the AFRIKATATERRE house in (GSEP, GEP, Bengueir). The considered specimen is a rectangular cavity, which is part of a set of two identical prefabricated structures, located at the International University of Rabat (UIR).
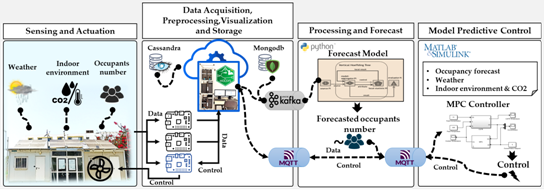
The holistic approach towards energy efficient buildings, is enabled by using several equipment together with their related hardware and software components. For instance, a weather station was built and installed on the roof of the EEBLab, next to the wind turbine and PV panels, to capture the relative humidity, ambient temperature, air pressure, solar radiation, wind direction and speed. To capture the temperature evolution of the EEBLab envelope, a prototype has been deployed to read sensors’ data installed in all walls of the EEBLab. The occupants’ number and presence IoT node was used to gather information about the number of occupants inside EEBLab. A comprehensive fine-grained occupancy information could be integrated to improve the performance of occupancy-driven control of HVAC, lighting, and ventilation systems.
HOLSYS - AFRIKATATERRE
For large-scale deployment, and with the aim to exploit and disseminate the know-how and knowledge gained in the framework of past projects, the UIR team has participated to the Solar Decathlon Africa (SDA) competition, which was held in Benguerir from 21st of August to 27th of September 2019, together with other students from UIR, Technische Hochschule Lübeck (THL) Germany, and a consortium of academic of Dakar.
The team designed, constructed, and deployed a smart and energy efficient house, named AFRIKATATERRE. Solar Decathlon Africa was an opportunity for the team’s members to test and deploy, on a large scale (i.e., in a real house), the developed technologies, approaches, and platforms.
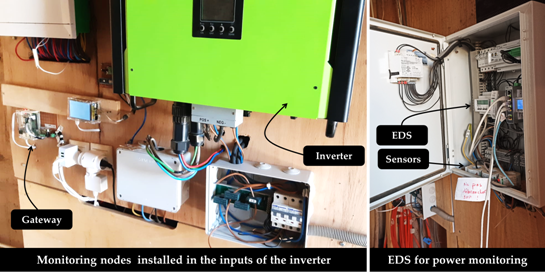
The holistic approach towards energy efficient buildings., was followed to deploy scenarios in AFRIKATATERRE. First, several IoT nodes developed for EEBLab were duplicated and deployed for the house, such as the weather station, indoor environment, and the gateways. Several other scenarios were developed later to connect the industrial Efficiency Data server (EDS) used to monitor the power metrics and the indoor environmental data. A gateway has been used to connect the EDS as well as the deployed nodes to the HOLSYS server, located in UIR facilities, for data visualization and storage.
It is worth noting that the AFRIKATATERRE house won the first prize in the Architecture contest and the second prize in the sustainability contest.

Request Access to Datasets
We offer access to some datasets for being used in the development of applications related to energy efficiency in buildings. Access to these datasets is granted on a per-request basis, once approved. Datasets are mainly designed to users that are interested in advancing sustainable and smart buildings through data-driven approaches.
-
Apply for Access Step 1Apply for access to those dataset using the button below "New use's account".
-
Personal Information Step 2Fill the form with your personal information.
-
Confirmation Email Step 3Once the request is approved, you will receive a confirmation email containing your account detail.
.